When improving legacy code, the goal is to move from a working but potentially messy state to a clean, maintainable system without breaking functionality. The safest way to do this is by making small, incremental changes while always keeping the system in a running state.
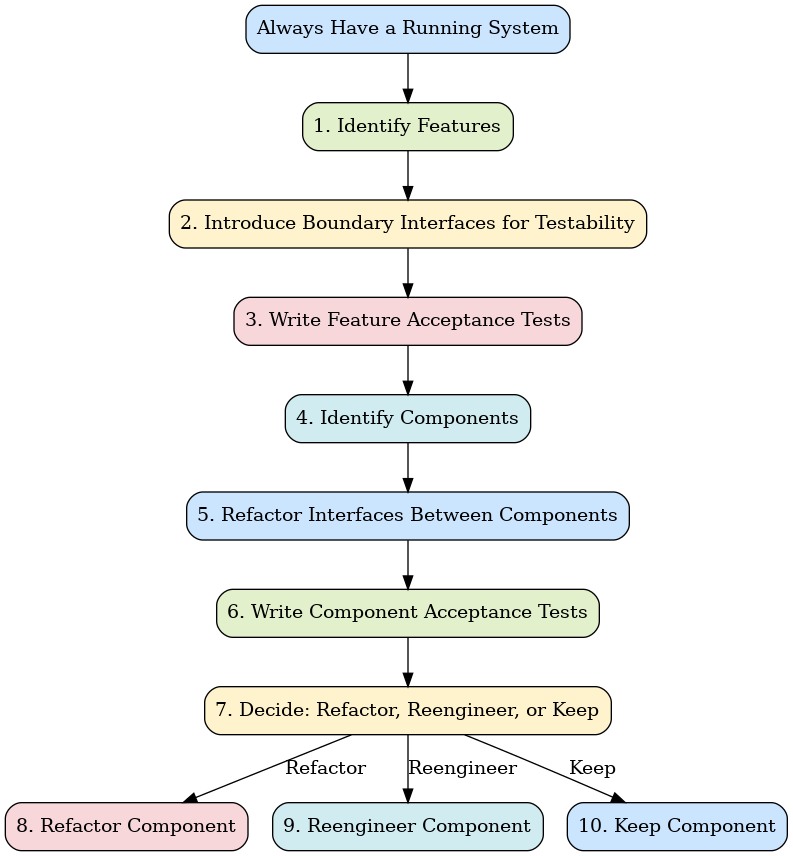
🚀 Always Have a Running System
Work in small steps and keep the application operational after each change. This reduces risk and makes debugging easier.
1️⃣ Identify Features
List all existing features in your codebase. Prioritise them based on:
Likelihood of future change
Risk of change (complexity, dependencies, business impact)
2️⃣ Introduce Boundary Interfaces for Testability
Refactor the system’s boundaries into clear interfaces. This allows you to simulate the environment using test doubles like fakes, mocks or stubs. Doing this early increases test coverage without needing a full system setup.
3️⃣ Write Feature Acceptance Tests
Before refactoring, cover important features with Acceptance Tests. These tests act as a safety net, ensuring that functionality remains intact while you change the code.
4️⃣ Identify Components
Break each feature into smaller components. Prioritise components the same way as features — by likelihood and risk of change.
5️⃣ Refactor Interfaces Between Components
Clean up or create interfaces so each component can be tested in isolation. This improves modularity and makes the system easier to maintain.
6️⃣ Write Component Acceptance Tests
For each component, write Acceptance Tests to verify its expected behaviour. This gives you confidence when refactoring or replacing it.
7️⃣ Decide for Each Component: Refactor, Reengineer or Keep
Refactor: Improve the internal design while keeping functionality the same
Reengineer: Rebuild the component entirely using ATDD (Acceptance Test Driven Development) or TDD (Test Driven Development)
Keep: Leave the component as is if it has few defects and will rarely change
8️⃣ Refactor Component
When refactoring, redesign classes step by step. Use unit tests to validate new designs and follow established Refactoring Patterns.
9️⃣ Reengineer Component
Re-implement the component from scratch using ATDD and TDD. This ensures a clean architecture and a fully tested implementation.
🔟 Keep Component
If a component is stable, rarely changes and has had few historical defects, you can safely keep it without modification.