When you're repaying a loan or credit, you might wonder how much you could save by paying early. But what if you don’t know the interest rate? You might only have three values: the loan amount, the monthly installment and the maturity (in months). In this article, we’ll walk through the math and JavaScript code required to compute early credit payments even without a given interest rate.
🧮 The Problem Breakdown
To calculate early repayment, you normally need the interest rate. But if it’s missing, we can still derive it using the loan amortization formula:
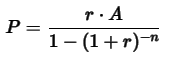
Where:
PPP: Monthly installment
AAA: Loan amount
rrr: Monthly interest rate (we’ll estimate this)
nnn: Number of months (maturity)
🔁 Estimating the Monthly Interest Rate
Since we cannot solve the formula for rrr algebraically, we use numerical approximation methods, like Newton-Raphson, to find the monthly interest rate.
🧑💻 JavaScript Code Implementation
Here’s a simple and customizable JavaScript implementation:
function estimateMonthlyInterestRate(P, A, n, guess = 0.01, tolerance = 0.000001, maxIterations = 1000) {
let r = guess;
for (let i = 0; i < maxIterations; i++) {
const f = (r * A) / (1 - Math.pow(1 + r, -n)) - P;
const df = (A * ((1 - Math.pow(1 + r, -n)) + (n * Math.pow(1 + r, -(n + 1))))) / Math.pow(1 - Math.pow(1 + r, -n), 2);
const newR = r - f / df;
if (Math.abs(newR - r) < tolerance) break;
r = newR;
}
return r;
}
function calculateEarlyPayment({ loanAmount, monthlyPayment, maturityMonths, monthsPaid }) {
const r = estimateMonthlyInterestRate(monthlyPayment, loanAmount, maturityMonths);
const remainingMonths = maturityMonths - monthsPaid;
// Remaining balance using amortization formula
const remainingBalance = (monthlyPayment * (1 - Math.pow(1 + r, -remainingMonths))) / r;
return {
monthlyRate: r,
remainingBalance: remainingBalance.toFixed(2)
};
}
// Example usage
const result = calculateEarlyPayment({
loanAmount: 10000,
monthlyPayment: 500,
maturityMonths: 24,
monthsPaid: 10 // User has paid 10 months
});
console.log("Estimated Monthly Interest Rate:", (result.monthlyRate * 100).toFixed(2) + "%");
console.log("Remaining Balance to Pay Off Now:", result.remainingBalance);
✅ What This Code Does
Estimates the monthly interest rate from known values.
Calculates the remaining balance based on how many months you’ve paid.
Assumes no prepayment penalty, adjust this if your bank charges one.
💡 Final Tips
If you’re developing a financial calculator, consider validating the output against real bank data.
Always inform users whether prepayment penalties or fees are included.
Add options for different compounding frequencies if needed (monthly, yearly, etc).
🧰 Useful Applications
Loan payoff calculators
Credit advisory tools
Fintech dashboards and simulations
📚 Summary
Even without knowing the interest rate, you can still calculate how much you owe if you decide to pay off a loan early. By reverse engineering the interest rate and using standard formulas in JavaScript, you can build a powerful and user-friendly repayment estimator.